About Us
Indian Council of Agricultural Research established Zonal Coordination Unit at Kanpur in 1979 to monitor transfer of technology projects. The Zonal Coordination Unit was upgraded as Zonal Project Directorate in March, 2009. Again it was upgraded as ICAR-Agricultural Technology Application Research Institute (ATARI). Presently, ICAR-ATARI, Kanpur is engaged in planning, monitoring, reviewing and supporting ICAR initiated technology dissemination projects mainly Krishi Vigyan Kendras in Uttar Pradesh.
The major functions of the ICAR-ATARI, Kanpur are:
- Planning, monitoring and reviewing of KVK activities in the zone; to identify, prioritize and implement various activities related to technology integration and dissemination
- Coordinating with SAUs, ICAR institutes/organizations, line departments and voluntary organizations in the zone for implementation of KVK mandated activities and
- Facilitating financial and infrastructural support to KVKs for effective functioning.
KVK and its mandate
In Zone-IV, 89 KVKs have been established by the ICAR in Uttar Pradesh.
The mandate of KVK is – Technology Assessment and Demonstration for its Application and Capacity Development (TADA-CD).
The activities of KVK include –
- On-farm testing to identify the location specificity of agricultural technologies under various farming systems.
- Frontline demonstrations to establish production potential of technologies on the farmers’ fields.
- Capacity development of farmers and extension personnel to update their knowledge and skills on modern agricultural technologies.
- To work as Knowledge and Resource Centre of agricultural technologies for supporting initiatives of public, private and voluntary sector in improving the agricultural economy of the district.
- Provide farm advisories using ICT and other media means on varied subjects of interest to farmers.
- To produce quality technological products (seed, planting material, bio-agents, livestock) and make it available to farmers, organize frontline extension activities, identify and document selected farm innovations and converge with ongoing schemes and programmes within the mandate of KVK.
KVKS IN UTTAR PRADESH AT A GLANCE
| No. of Districts in UP | No. of KVKs under | Total KVKs | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAU | ICAR | NGO | Other(Educational) | ||
| 75 | 67 | 7 | 12 | 3 | 89 |
HOST INSTITUTION WISE LIST OF KVKS WITH THEIR ESTABLISHMENT YEAR
| S.N. | Name of the KVK NDUA & T,Ayodhya |
Year of establishment | S.No. | Name of the KVK | Year of establishment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Bahraich | 1983 | 13 | Balrampur | 2005 |
| 2 | Ballia | 1989 | 14 | Chandauli | 2005 |
| 3 | Basti | 1984 | 15 | Jaunpur-I | 2005 |
| 5 | Mau | 1989 | 16 | SantKabir Nagar | 2009 |
| 5 | Varanasi | 1989 | 17 | Ambedkar Nagar | 2010 |
| 6 | Siddhharthnagar | 1992 | 18 | Amethi | 2018 |
| 7 | Ayodhya | 2004 | 19 | Bahraich-II | 2018 |
| 8 | Gorakhpur | 2004 | 20 | Gonda-II | 2018 |
| 9 | Maharaj ganj | 2004 | 21 | Sultanpur-II | 2018 |
| 10 | Sonbhadra | 2004 | 22 | Jaunpur-II | 2018 |
| 11 | Azamgarh-I | 2004 | 23 | Ghazipur-II | 2018 |
| 12 | Barabanki | 2004 | 24 | Shravasti | 2020 |
| 25 | Azamgarh-II | 2021 | |||
| CSAU&T, Kanpur | |||||
| 26 | Raebareli | 1984 | 33 | Firozabad | 2004 |
| 27 | Fatehpur | 1989 | 34 | LakhimpurKheri | 2005 |
| 28 | Aligarh | 1992 | 35 | Farrukhabad | 2005 |
| 29 | Kannauj | 2004 | 36 | Hardoi | 2005 |
| 30 | Etawah | 2004 | 37 | Mahamaya Nagar | 2009 |
| 31 | Mainpuri | 2004 | 38 | Kasganj | 2018 |
| 32 | Kanpur Dehat | 2004 | 39 | Raebareli-2 | |
| BUAT, Banda | |||||
| 40 | Jhansi | 1984 | 43 | Jalaun | 2005 |
| 41 | Mahoba | 2004 | 44 | Lalitpur | 2005 |
| 42 | Hamirpur | 2005 | 45 | Banda | 2007 |
| 46 | Prayagraj-II | 2020 | |||
| SVPU &T, Meerut | |||||
| 47 | Bijnor | 1992 | 57 | Moradabad | 2005 |
| 48 | Rampur | 1992 | 58 | Gautam Buddha Nagar | 2005 |
| 49 | Badaun-I | 1992 | 59 | Bulandshahar | 2004 |
| 50 | Saharanpur | 1992 | 60 | Badaun-II | 2018 |
| 51 | Ghaziabad | 1992 | 61 | Sambhal | 2018 |
| 52 | Sahajahanpur | 194 | 62 | Shamli | 2018 |
| 53 | Meerut | 1994 | 63 | Amroha | 2018 |
| 54 | Muzaffarnagar-I | 1994 | 64 | Hapur | 2018 |
| 55 | Pilibhit | 1998 | 65 | Muzaffarnagar-II | 2019 |
| 56 | Baghpat | 2004 | 66 | Moradabad | 2020 |
| U.P. Pt. DeenDayalUpadhyayaPashuChikitsaVigyanVishwaVidyalayaEvam Go AnusandhanSansthan, Mathura | |||||
| 67 | Mathura | 1984 | |||
| Kamla Nehru Memorial Trust, Sultanpur | |||||
| 68 | Sultanpur | 1976 | |||
| RBS College, Agra | |||||
| 69 | Etah | 1992 | 70 | Agra | 2002 |
| BHU, Varanasi | |||||
| 71 | Mirzapur | 1984 | |||
| Deendayal Research Institute, Gonda | |||||
| 72 | Gonda | 1989 | 73 | Chitrakoot | 1992 |
| SHIAS&T, Allahabad | |||||
| 74 | Prayagraj-I | 1992 | |||
| Raja Avadesh Singh Memorial Society,Pratapgarh | |||||
| 75 | Pratapgarh | 1999 | |||
| Kunwar Ram Bux Singh Educational Sociaty, Lucknow | |||||
| 76 | Unnao | 1999 | |||
| Indian Veterinary Research Institute, Bareilly | |||||
| 77 | Bareilly | 1985 | |||
| Indian Institute of Sugarcane Research, Lucknow | |||||
| 78 | Lucknow | 1994 | 79 | Lakhimpur Kheri-II | 2019 |
| Post Graduate College, Gazipur | |||||
| 80 | Gazipur | 2002 | |||
| Indian Institute of Vegetables Research, Varanasi | |||||
| 81 | Kushinagar | 2005 | 82 | Deoria | 2009 |
| Indian Institute of Seed Science,Mau | |||||
| 83 | At. Ravidas Nagar | 2008 | |||
| Manav Vikas Evam Seva Sansthan, Lucknow | |||||
| 84 | Sitapur-I | 2005 | |||
| Dr. Bhimrao Ambedkar Welfare Society, Allahabad | |||||
| 85 | Kaushambi | 2006 | |||
| SarpanchSamaj, New Delhi | |||||
| 86 | Auraiya | 2007 | |||
| Ranvir Rananjay Degree College Association,Sultanpur | |||||
| 87 | Sitapur-II | 2011 | |||
| Guru GorakshnathSewa Sansthan | |||||
| 88 | Gorakhpur-II | 2016 | |||
| ICAR-Central Soil Salinity Research Institute,Karnal | |||||
| 89 | Hardoi-II | 2018 | |||
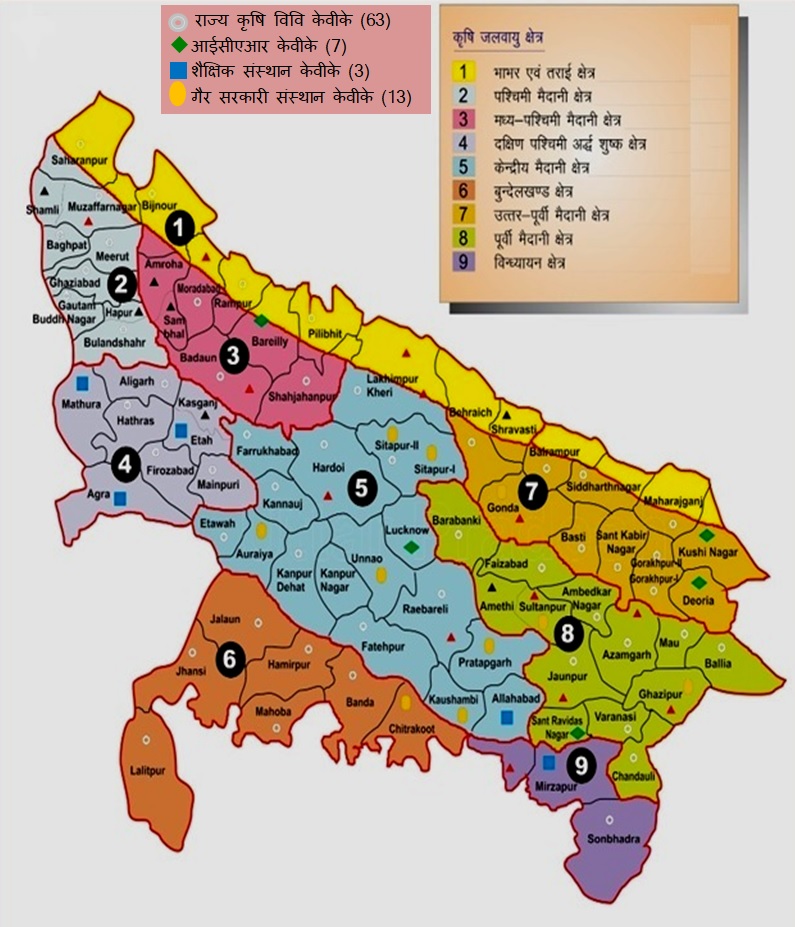
AGRO-CLIMATIC ZONES
Uttar Pradesh is divided into 9 agro climatic zones (South Western Semi Arid, Bhabhar and Tarai, Western Plain, Mid Western Plain, Central Plain, Bundelkhand, North Eastern Plain, Eastern Plain and Vindhyan Zone), depicted as in figure1.
Distribution of KVKs (89) in Uttar Pradesh
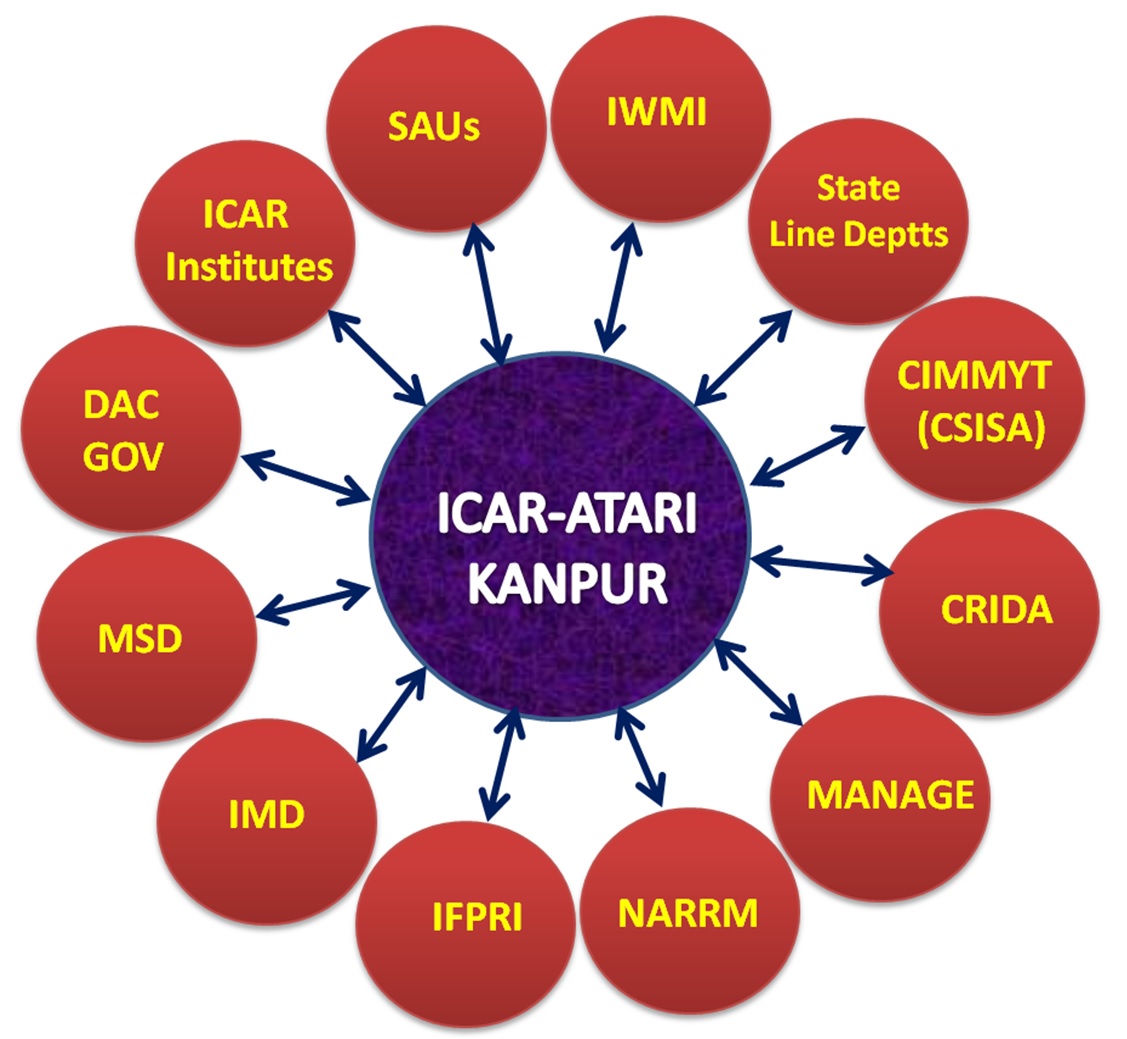
LINKAGES AND COORDINATION
- SAUs (SVBPUAT, CSAUAT, NDUAT& BUAT) linked for technological backstopping to KVKs of Uttar Pradesh
- Linkage with MANAGE Hyderabad for Agri-business &Agri Clinic Scheme & also knowledge up gradation of KVK staff in ICT.
- Interface on KVK-ATMA linkage held at State level with Principal Secretary Agriculture & Director Agriculture for effective linkage.
- IIVR, Varanasi for providing suitable technologies for vegetable production.
- Linkage with CRIDA, Hyderabad for promoting climate resilient technologies in 11 districts of U.P.
- Fodder development programme initiated in collaboration with IGFRI, Jhansi.
- Linkage with National Rain fed Area Authority for development of Bundelkhand region.
- Senior level interactions and meetings organized with line department officials for better convergence & linkage.